Statistical Innovation: ECLAC Promotes the Use of Non-Traditional Sources to Improve Regional Analysis
Work area(s)
Through the innovative use of satellite and geospatial data, statistical, geographic, and Earth observation information has been effectively integrated at the subnational level, significantly enriching the territorial, environmental, and socioeconomic analysis of Latin America and the Caribbean.
In its ongoing efforts to strengthen statistical production and provide more accurate, timely, and detailed information on the regional reality, ECLAC’s Statistics Division has intensified the development of indicators based on non-traditional data sources.
The use of satellite data in the context of sustainable development offers key advantages, such as continuous availability, the ability to generate time series to assess changes over time, and the possibility of comparing results across different subnational areas and countries. In addition, access to these data comes at a relatively low cost, which facilitates the continued provision of accurate information to support sustainable development initiatives.
By applying techniques to process, analyze, and transform raw satellite-acquired data, derived products are generated that enhance the available information. The automation of extraction, transformation, and loading processes ensures the sustainability of time series dissemination, minimizing the need for manual intervention for each data entry.
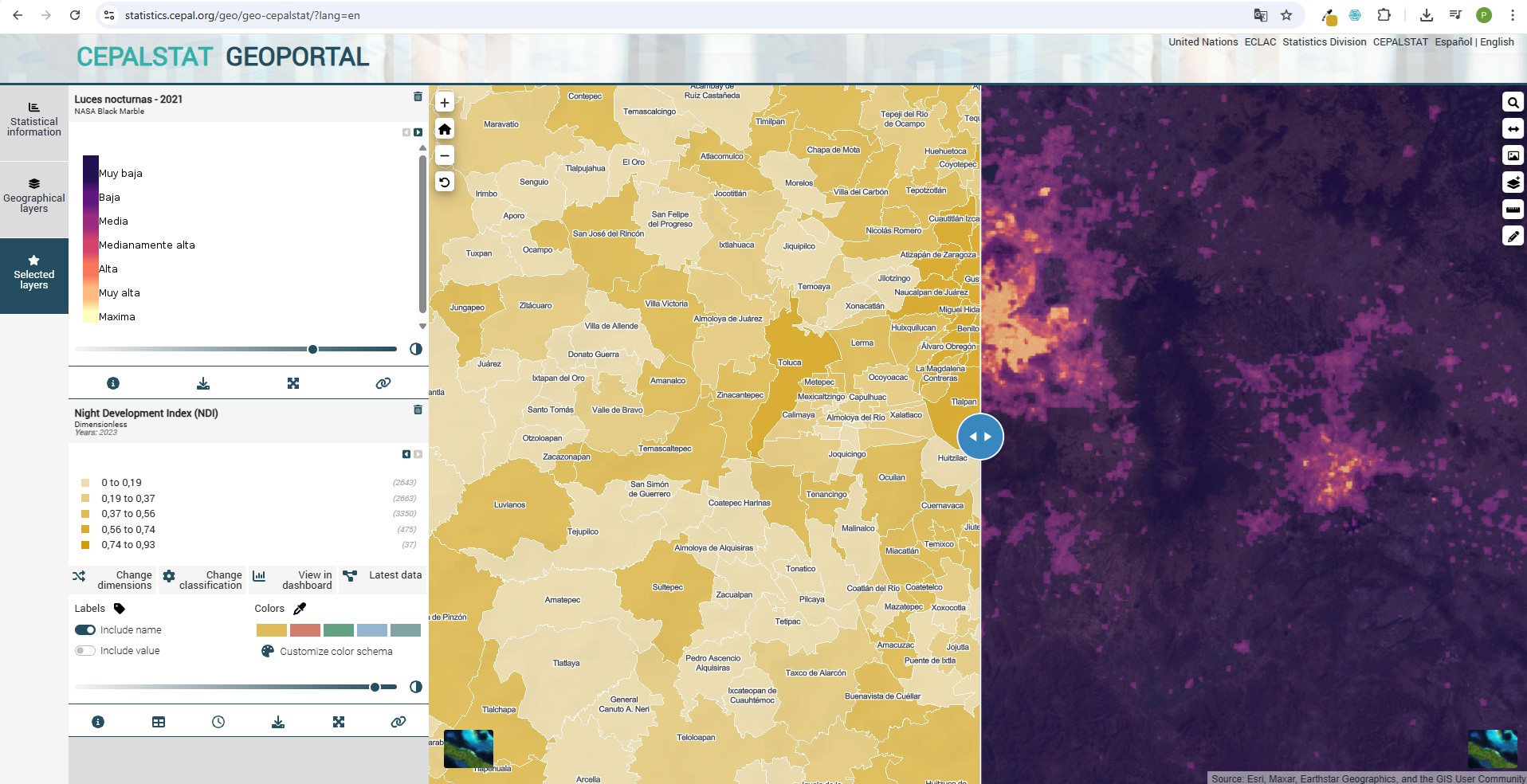
One of the main advantages of these data, enriched with geographic information, is that they provide spatial context, revealing patterns and relationships between variables. This allows for a deeper understanding of territorial phenomena and supports the design of more effective sustainability strategies. It also enables the creation of new statistical indicators at a more detailed and precise scale, offering a more comprehensive and dynamic view of key phenomena such as human settlements, land cover and use, and climate change. Moreover, the processing of these sources generates geospatial datasets presented as geographic layers.
These new indicators and geographic layers, available for public consultation, help improve the understanding of phenomena such as urban expansion, the growth of human settlements, population distribution, energy efficiency, economic dynamism of cities, and activity patterns in urban centers. Likewise, statistics on land use, forest cover, and bodies of water are essential to understanding how natural resources are distributed and used in different regions, providing key data for public policy formulation, scientific research, and environmental management.
Statistical indicators can be visualized and downloaded on CEPALSTAT, while the geographic layers can be accessed through the CEPALGEO portal catalog and either displayed on its geoportal or downloaded for use in a desktop Geographic Information System environment.
This first exercise incorporating satellite and geospatial sources into statistical production establishes a technical foundation within the organization for the future use of these inputs, aiming to meet the growing need for more territorially disaggregated information. It also reaffirms the Commission’s commitment to the modernization of information systems and its strategic role in generating data that respond to increasing demands for more effective and sustainable public policies.